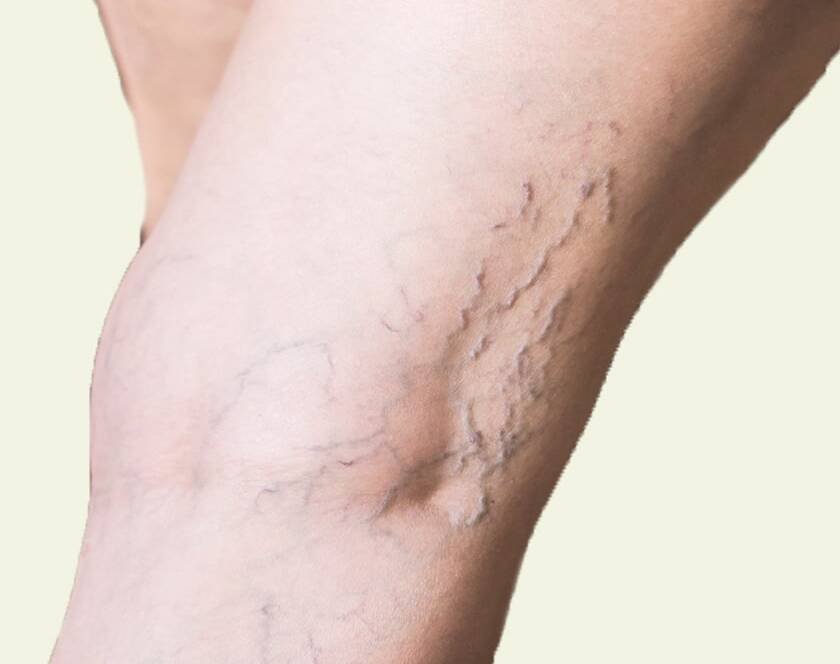
Chronic non-healing ulcers are open sores or wounds that do not heal within a reasonable amount of time, and can be caused by a variety of factors such as poor circulation, diabetes, peripheral arterial disease, and venous insufficiency. These ulcers can be a source of chronic pain and may lead to serious complications such as infection and amputation.
The management of chronic non-healing ulcers involves a multidisciplinary approach that includes:
Wound care: This includes cleaning the ulcer and applying topical wound dressings to promote healing and prevent infection.
Compression therapy: This involves wearing compression stockings or bandages to help improve circulation and reduce swelling.
Offloading: Using special devices such as casts, shoes or crutches to reduce weight-bearing on the affected area
Medications: Antibiotics may be prescribed if an infection is present, and other medications may be used to manage underlying conditions such as diabetes or peripheral arterial disease.
Debridement: removal of dead or damaged tissue surrounding the wound
Nutrition management: to ensure that the patient is getting the necessary nutrients to promote healing
Physical therapy: to help improve mobility and prevent muscle atrophy
Psychological support: the chronic nature of these ulcers can cause emotional distress,
It is important to note that the healing of chronic non-healing ulcers can be a slow process and may take several weeks or months. It’s important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the best treatment option for your individual needs and goals.
If you have any questions regarding our services, please contact us or call at +91 9879546805.
Hear from our patients
EXCELLENTTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Had a vericose vein surgery for both legs.such a supportive doctors and team.Special Thanks to Dr.Aashutosh shah,sunnybhai and all the staff members for wondrful service.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Thank you sir your treatment is very goodTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Very happy.. Very good service.. Very good staff..Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Amazing staff, totaly supportive. Dr ashutosh sir & his Team totaly take care of the patients & does the procedure properly
Frequently Asked Questions
Having doubts and questions? These are few questions our customers normally ask us!
What is the purpose of hymenoplasty surgery?
Hymenoplasty is performed to reconstruct the hymen, which may be desired for cultural, religious, or personal reasons.
Can the hymen grow again?
The hymen does not regrow naturally; however, hymenoplasty surgically restores its presence.
Why is my hymen not opening?
Variations in hymen elasticity and opening are normal. If there are concerns, it’s best to consult a gynecologist.
Can a girl bleed after hymenoplasty?
Some bleeding is possible after hymenoplasty, similar to what might occur with the initial breaking of the hymen.
Can hymen bleed 2 times?
The hymen can only bleed once naturally. Post-hymenoplasty, it may bleed again upon rupture.
Does hymenoplasty restore virginity?
Hymenoplasty reconstructs the hymen physically but does not ‘restore’ virginity in a biological sense.
How many times can hymen bleed?
The hymen typically bleeds once upon tearing. After hymenoplasty, it may bleed again if ruptured.
Can a non-virgin bleed again?
Post-hymenoplasty, a woman may experience bleeding upon the hymen’s rupture, similar to the first time.
Is it necessary to bleed on the first night?
Bleeding is not a universal indicator of virginity or sexual experience. It varies among individuals.
How can a husband know that his wife is not a virgin?
Virginity cannot be determined physically. It’s a personal aspect that relies on trust and communication.
How long does hymen take to heal?
The healing time for hymenoplasty is typically around 6-8 weeks, but it can vary.
Do boys bleed on the first night?
Boys do not experience bleeding related to virginity.
Did your wife bleed on the first night?
This is a personal and private matter, and bleeding is not a definitive indicator of virginity.
Can you bleed if your partner is too big?
Bleeding can occur due to various reasons, including the size of the partner, but it’s not a certainty.
Contact Us
Ready to discuss? Fill out our contact form for a confidential consultation.